There are numerous applications of opinion surveys. Common ones are:
- Soliciting the views of customers on a planned or existing product, service, or system/ organization;
- Assessing the satisfaction of customers;
- Measuring the loyalty or engagement of the workforce; and
- Asking suppliers to evaluate the quality of their relationship with the organization.
The outcomes of successful opinion surveys are opportunities for improvements (OFIs) and initiatives. Often times such OFIs and initiatives are further defined through well-planned discussion groups of the survey results.
There are three types of opinion surveys:
• One-dimensional (1-D) opinion surveys, where respondents are only asked to cast their opinion; e.g., on a 7-point Likert Scale, regarding specific attributes of an entity; as shown below:
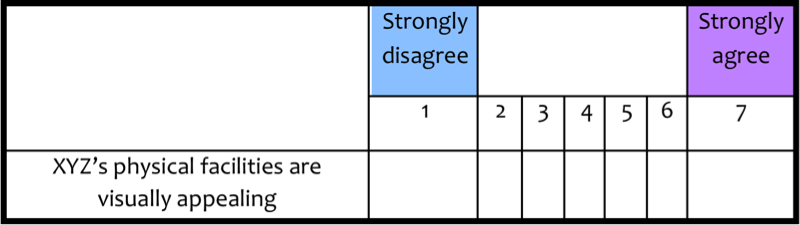
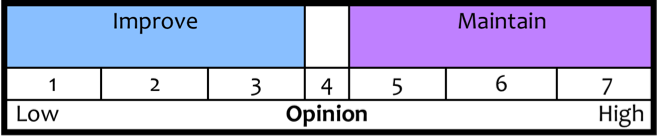
A corresponding action model is used for the interpretation of results; where, for example, an average score of 1.5 indicates the need to improve. It is important to note, however, that the survey results do not generally recommend specific action(s) to remedy the situation.
• Two-dimensional (2-D) opinion surveys, where respondents are additionally asked to rate the importance of each attribute, as shown below.
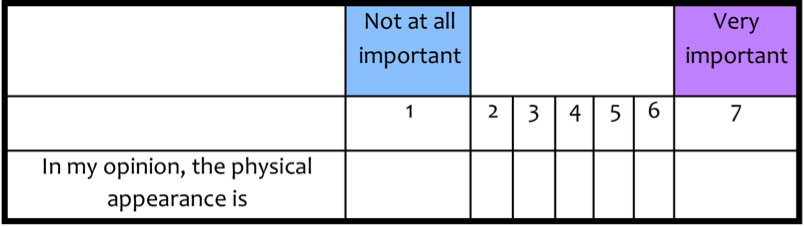
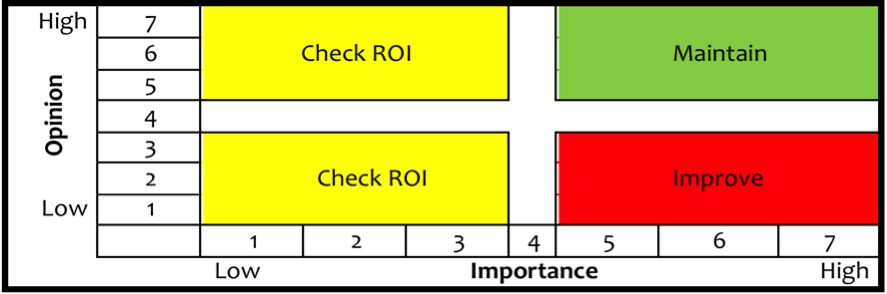
The results on both the opinion and importance can be used independently to provide indication of priority as shown in the action model below.

Alternatively, the opinion and importance results can be used jointly, as shown in the action model below:
• Three-dimensional opinion surveys, where respondents additionally compare with a competing organization, as shown below:
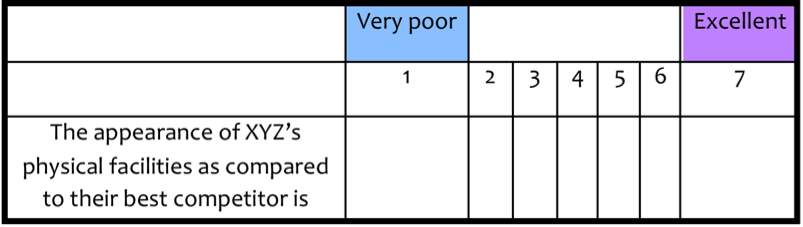
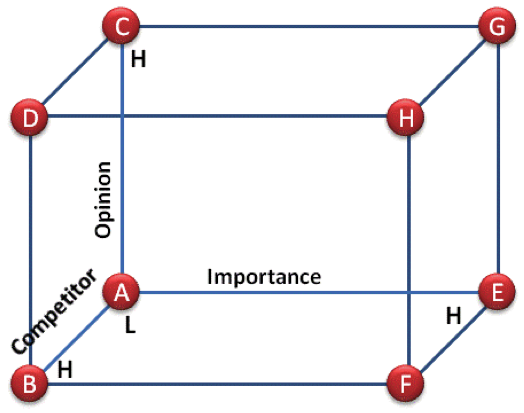
The following cube provides an action model based on the results of a 3-D survey.
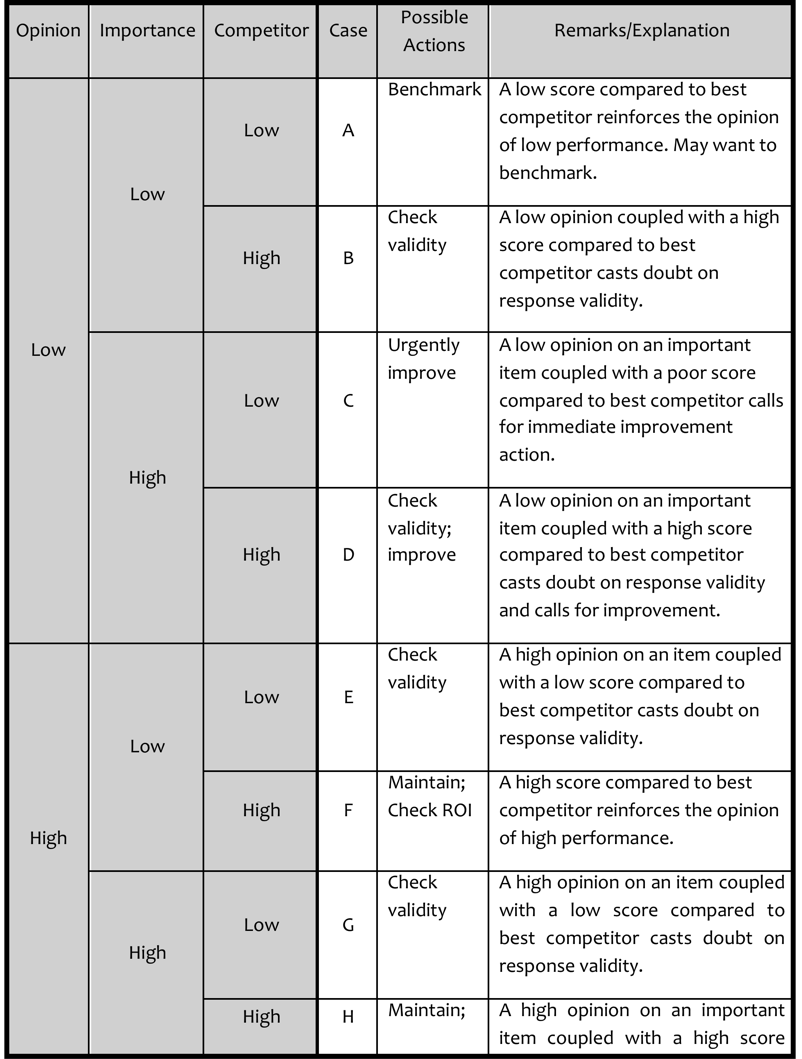
A matrix may be developed to guide possible actions based on the 3-D cube model as shown in the table below:
CREDITS: Dr. Tariq A. Aldowaisan